Introduction
A large number of liquids retaining tanks are used for storing the water, oil or chemical fluids. These can have circular or rectangular shape in plan and can be built either above or below the ground. The overhead service reservoirs are a common sight. The tanks used for water storage are generally placed at a certain height in order to get the sufficient heads for water supply and firefighting. For this purpose, the tanks are either installed at top of building or at top of supporting structure, which could be in form of shaft or frame type.
Type of Tanks
On basis of position from ground level
Underground Tank
Tanks resting on ground
Elevated/ Overheads tanks
On basis of shape
Circular shaped tanks
Rectangular shaped tanks
Spherical shaped tanks
Intze type tanks
Intze type Tank
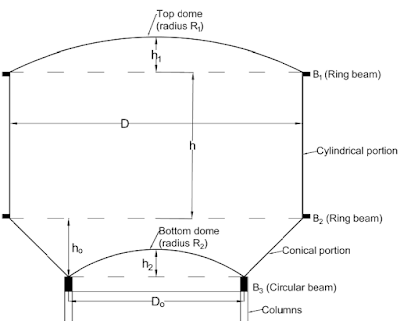
The Intze type water tank got its name due to special arrangement of conical dome and bottom dome. In this particular arrangement, the inward force from conical dome and outward force from bottom dome balances out each other to a greater extent at section where conical dome and bottom dome meets which leads to lesser section sizes and reinforcement requirement in intze case while comparing to other shapes. The various components of an overhead water tank are shown and described as below:
i) Water tank portion with
a) Roof
b) Walls
c) Ring beams
c) Floor or bottom slab
d) Floor beams including circular beams
ii) Staging portion, includes
a) Columns
b) Bracing
c) Foundation
a) Top Dome: The top dome serves as covering to top of tank. It also provides the surface to person to clean the tank. Lightening conductor and aviation light are placed on the dome. If the sloshing wave height is greater than the free board, then the top dome is designed for the effective upward pressure. Otherwise, minimum reinforcement is provided in top dome. The thickness usually lies between 100 mm to 150 mm and the rise is about 1/5th of the span.
b) Upper Ring beam: The ring beam is present at junction of top of cylindrical wall and dome edges. The horizontal component of the thrust is transferred to the beam from dome. The ring beam is designed to resist the hoop tension.
c) Cylindrical walls: The wall lies in between the upper and lower ring beam. The wall transferred the vertical load from dome to lower ring beam. The wall is designed for hoop tension induced due to horizontal water pressure.
d) Bottom Ring beam: The bottom ring beam is present at the junction of the cylindrical walls and the conical wall. The bottom ring beam resist the horizontal component of the reaction of the conical wall acting on the cylindrical wall. The ring beam will be designed for same.
e) Conical Wall: The conical wall is designed for hoop tension due to water pressure. The wall will also be designed as a slab spanning between the bottom ring beam at top and the circular ring beam (resting on top of columns) at bottom.
f) Bottom Dome: The bottom dome is supported on the circular ring beam. The dome is designed as slab for vertical load of water.
g) Circular Beam: The circular beam is designed to support the entire tank with its content inside. The beam will be supported on columns and should be designed for resulting bending moment and torsion.
h) Staging: The staging portion includes columns and bracing beam. Columns are designed to transfer the total load including their self-weight to the foundation. Bracing beams are provided at regular intervals to brace columns and have to be designed for wind pressure or seismic loads whichever governing.










2 Comments
Horizontal tanks are steel horizontal storage units used for a variety of fluids. Utilized across numerous industries, from chemical to agriculture, they ensure safety and efficiency in storage. These tanks are essential for managing large volumes of liquids and contribute significantly to operational efficiency.
ReplyDeleteCiekawe, dobrze zaprojektowane
ReplyDeletespolshy